There is 2 types of lightning strikes : Upwards and downwards, defined by the direction of the leader (initiation of the lightning, preparing the way until the lightning)
The names of the cloud-to-ground lightning flashes depend on the polarity and orientation of the first leader.
So, we have :
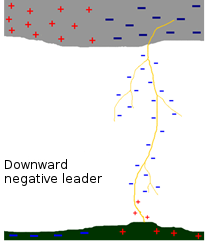
The downward negative leader comes from a downward leader from negative layer in lightning cloud, spreading to the ground with 70 to 1200 km/s velocity.
Nearby, an upward leader is generated. When they meet, the discharge occurs by electrons transfer from the cloud to the ground. These are the most common type.
The upward negative leader comes from an upward negative charge. This upward leader travels from 80 to 460 km/s velocity.
As for all upward charges, it starts from a sharp of the ground (mountain, telecommunication tower,…) and spreads until a cloud area charged positively. With low distance, a downward leader is generated from a cloud. When the contact is made, the positive charges are transferred from the cloud to the ground.
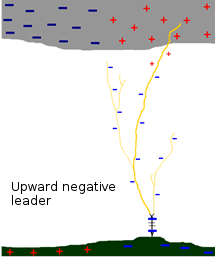
Le coup de foudre ascendant négatif provient d’une charge ascendante négative. Ce traceur ascendant voyage à une vitesse voisine de 80 à 460 km/s. Comme toutes les charges ascendantes, il débute à partir d’une aspérité au niveau du sol (montagne, antenne de télécommunication,…) et se propage vers une zone du nuage chargée positivement. A faible distance, un traceur descendant est émis à partir du nuage.
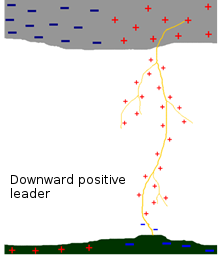
The upward positive leader starts from an upward leader moving with 40 to 70 km/s velocity near the ground, and which can reach until 1000 km/s altitude.
This leader comes from an upward positive leader from the ground. These leaders will spread until the base of the cloud positively charged. When approaching, the discharge occurs and the electrons are transferred from the cloud to the ground.
Discover our E.S.E. Air Terminals
